K. lactis Protein Expression Kit
Product information| Code | Name | Size | Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
E1000S |
K. lactis Protein Expression Kit |
- | Unavailable in your region |
K. lactis Protein Expression Kit
We are excited to announce that all reaction buffers are now BSA-free. NEB began switching our BSA-containing reaction buffers in April 2021 to buffers containing Recombinant Albumin (rAlbumin) for restriction enzymes and some DNA modifying enzymes. Find more details at www.neb.com/BSA-free.
Product Introduction
The K. lactis Protein Expression Kit provides an easy method for expressing a gene of interest in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Proteins may be produced intracellularly or secreted using an integrative expression vector (pKLAC2). To achieve protein secretion, a gene of interest is cloned downstream of the K. lactis α-mating factor secretion domain, which is eventually processed in the Golgi and results in secretion of the desired protein.
- Supplied with competent K. lactis cells (NEB# C1001)
- Allows cloning and expression of genes toxic to E. coli
- Rapid high cell density growth results in high yield protein expression
- Easy-to-use protocols for those inexperienced with yeast systems
- No expensive antibiotics or methanol required
- Attractive commercial sub-licensing
| Catalog # | Size | Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| E1000S | 1 set |
- Product Information
- Protocols, Manuals & Usage
- Tools & Resources
- FAQs & Troubleshooting
- Citations & Technical Literature
- Quality, Safety & Legal
- Other Products You May Be Interested In
Product Information
Description
Highlights
The K. lactis Expression Kit provides an easy method for expressing a gene of interest in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis (Figure 1). Proteins may be produced intracellularly or be secreted using the supplied integrative expression vector pKLAC2 (Figure 3). To achieve protein secretion, a gene of interest is cloned downstream of the K. lactis α-mating factor secretion domain (α-MF; Figure 4) which is eventually processed in the Golgi resulting in secretion of the desired protein (Figure 1).The K. lactis expression system offers several advantages over other yeast and bacterial protein expression systems. First, K. lactis has been used to produce proteins at industrial scale in the food industry for over a decade due to its ability to rapidly achieve high culture densities and abundantly produce recombinant proteins (Figure 2). Second, yeast expression is driven by a variant of the strong LAC4 promoter that has been modified to lack background expression in E. coli (1). Therefore, genes toxic to E. coli can be cloned into pKLAC2 in bacteria prior to their expression in yeast. Third, the kit includes highly competent K. lactis cells making the technology easy-to-use for those not accustomed to working with yeast. Their high transformation efficiency makes the system suitable for methods that require large numbers of transformants, for example, expression cloning using cDNA libraries. Selection of yeast transformants uses a unique antibiotic-free method in which acetamidase (amdS) expressed from pKLAC2 permits transformed cells to utilize acetamide as a sole nitrogen source on defined medium. Acetamide selection promotes formation of cells containing multiple integrations of pKLAC2 which results in higher yields of protein. Finally, proteins expressed in K. lactis have access to eukaryotic protein folding and glycosylation machinery that E. coli cells do not possess, making it an important alternative to bacterial expression systems.
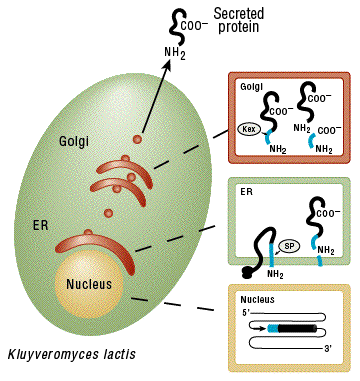
Secreted protein processing. In the nucleus, an integrated expression vector encoding a fusion between the α-MF domain (blue) and a desired protein (black) is expressed. A signal peptide in the α-MF domain directs entry of the fusion protein into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and is removed by signal peptidase (SP). The fusion protein is transported to the Golgi where the Kex protease removes the α-MF domain. The protein of interest is then secreted from the cell.
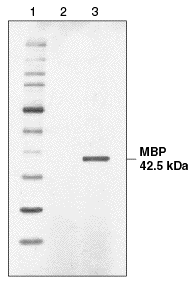
SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis separation of secreted recombinant maltose binding protein (MBP) and detection by Coomassie staining. Lane 1: Protein Molecular Weight Markers. Lane 2: spent culture medium (15 µl) from wild-type K. lactis cells. Lane 3: spent culture medium (15 µl) from K. lactis cells harboring an integrated expression cassette containing the E. coli malE gene.
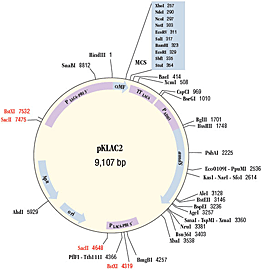
Figure 4:

- This product is related to the following categories:
- Protein Expression in Yeast,
- Protein Expression,
- This product can be used in the following applications:
- Protein Expression in Yeast ,
- Protein Expression
Kit Components
Kit Components
The following reagents are supplied with this product:
| NEB # | Component Name | Component # | Stored at (°C) | Amount | Concentration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Properties & Usage
Shipping Notes
- Ships on dry ice
Features
- High level and scalable expression of recombinant proteins
- Rapid high cell density growth
- Simultaneous expression of multiple proteins possible
- No background gene expression during E.coli cloning steps
- Easy and fast cell transformation procedure
- Antibiotic-free selection
Related Products
Companion Products
Product Notes
- NEB 5-alpha Competent E. coli (High Efficiency) (NEB #C2987), NEB 5-alpha Electrocompetent E. coli (NEB #C2989) and NEB 5-alpha Competent E. coli (Subcloning Efficiency) (NEB #C2988) are all recommended for propagation and subcloning pKLAC1 control plasmid and pKLAC2 vector.
References
- Colussi, P.A. and Taron, C.H. (2005). Appl. Environ. Microbiol.. 71,
- Looke, M. et. al (2011). Biotechniques. 50, 325-328.
- van Ooyen, A.J.J.et al. (2006). FEMS Yeast Research . 6, 381-392.
- Spohner, S.C. et.al (2016). J Biotechnol. 222, 104-116.
- Chuzel, L., Ganatra M.B. et. al (2017). Genome Announc. 5, e00623-17.
- Read, J.D.et al. (2007). Appl. Environ. Microbiol.. 73, 5088-5096.
- Platko, J.D.et al. (2008). Protein Expr. Purif.. 57, 57-62.
- Ekborg, N.A.et al. (2007). Appl. Environ. Microbiol.. 73, 7758-7788.
- Foster, J.M. et. al (2008). Parasitol Res.. 104(5), 1047.
- Vainauskas, S., Taron, C.H. (2016). New England Biolabs Application Note.
Protocols, Manuals & Usage
Protocols
- Protein expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Linearization of pKLAC2 for integrative transformation of K. lactis.
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Identification of Multi-copy Integrants
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Identification of properly integrated cells
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Simultaneous Expression of Multiple Proteins
- Protein expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Cloning a PCR fragment into pKLAC2 (E1000).
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Growth of strains for detection of secreted protein
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Transformation of K. lactis GG799 cells
Manuals
Application Notes
Tools & Resources
Selection Charts
FAQs & Troubleshooting
FAQs
- What systems does NEB offer for protein expression and purification?
- I received my kit and don’t see any competent cells or transformation reagent. Where are they?
- I’ve expressed my protein, now how do I purify it?
- I’ve noticed untransformed K. lactis will grow when streaked on the selection media. Is the selection not working?
- Where can I find more detailed FAQs for the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit?
- Can you tell me more about the switch from BSA to Recombinant Albumin (rAlbumin) in NEBuffers?
Tech Tips
NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Cloning Kit (NEB #E5520) or the Gibson Assembly Cloning Kit (NEB #E5510) are excellent ways to assemble a linear yeast expression cassette. (See "Improved method for assembly of linear yeast expression cassettes using NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix" in the Application Notes section under the Other Tools and Resources tab)
Citations & Technical Literature
Citations
Additional Citations
Publications
- Chuzel, L., Ganatra, M.B., Schermerhorn, K.M., Gardner, A.F., Anton, B.P., Taron, C.H. (2017) Complete genome sequence of Kluyveromyces lactis strain GG799, a common yeast host for heterologous protein expression Genome Announc; 5(30), PubMedID: 28751387
- Sakhtah, H., Behler, J., Ali-Reynolds, A., Causey, T.B., Vainauskas, S., Taron, C.H. (2019) A novel regulated hybrid promoter that permits autoinduction of heterologous protein expression in Kluyveromyces lactos Appl Environ Microbiol; pii: e00542-19. PubMedID: 31053583
Quality, Safety & Legal
Quality Assurance Statement
Quality Control tests are performed on each new lot of NEB product to meet the specifications designated for it. Specifications and individual lot data from the tests that are performed for this particular product can be found and downloaded on the Product Specification Sheet, Certificate of Analysis, data card or product manual. Further information regarding NEB product quality can be found here.Specifications
The Specification sheet is a document that includes the storage temperature, shelf life and the specifications designated for the product. The following file naming structure is used to name these document files: [Product Number]_[Size]_[Version]Safety DataSheets
The following is a list of Safety Data Sheet (SDS) that apply to this product to help you use it safely.SacII
pKLAC1-malE Control Plasmid
pKLAC2 Vector
rCutSmart™ Buffer
Yeast Carbon Base Medium Powder (12 g)
Acetamide solution (sterile) (10 ml)
K. lactis GG799 Competent Cells
NEB® Yeast Transformation Reagent (5 ml)
Legal and Disclaimers
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.
New England Biolabs (NEB) is committed to practicing ethical science – we believe it is our job as researchers to ask the important questions that when answered will help preserve our quality of life and the world that we live in. However, this research should always be done in safe and ethical manner. Learn more.
Licenses
Notice to Buyer/User: The K. lactis Protein Expression Kit was developed from basic research at New England Biolabs, Inc. and DSM Biologics Company B.V. The buyer and user has a non-exclusive sublicense to use this system or any component thereof, including the K. lactis GG799 Competent Cells, for RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY. A license to use this system for manufacture of clinical grade material or commercial purposes is available from New England Biolabs, Inc., or DSM Biologics Company B.V.Other Products You May Be Interested In
The supporting documents available for this product can be downloaded below.




