PURExpress® Δ Ribosome Kit
Product information| Code | Name | Size | Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
E3313S |
PURExpress Delta Ribosome Kit |
10 rxns | - | Unavailable in your region |
PURExpress® Δ Ribosome Kit
Product Introduction
PURExpress® delta ribosome kit is a variation of the PURExpress In vitro Protein Synthesis Kit where ribosomes are omitted from the translation mix.
- Control ribosomes provided separately
- Designed for use with your own ribosomes
- User supplied ribosomes can be E. coli-based wild type, mutant or ribosome from other bacterial species
- Convenient for directly assaying ribosomal activity and translation studies
| Catalog # | Size | Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| E3313S | 10 reactions |
- Product Information
- Protocols, Manuals & Usage
- Tools & Resources
- FAQs & Troubleshooting
- Citations & Technical Literature
- Quality, Safety & Legal
- Other Products You May Be Interested In
Product Information
Description
Highlights
- Cleaner System - sample degradation eliminated
- Easy-to-use - protein expression complete in approximately two hours
- Simple Analysis - protein can often be visualized directly on a Coomassie stained gel
PURExpress Citations
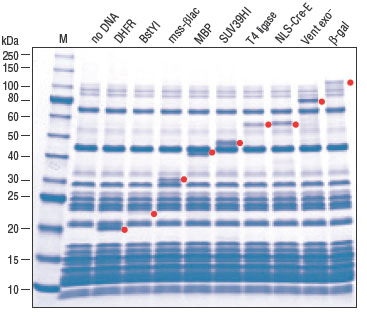
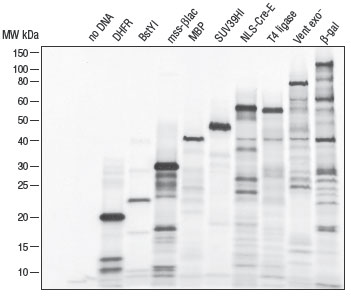
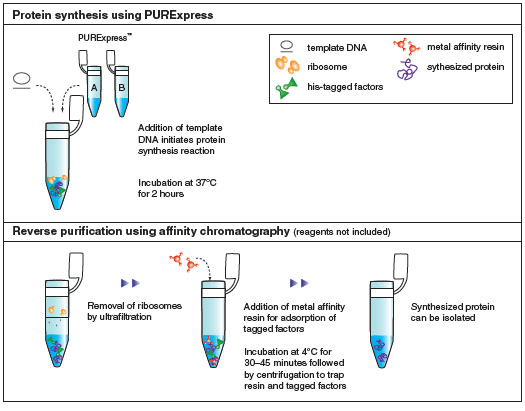
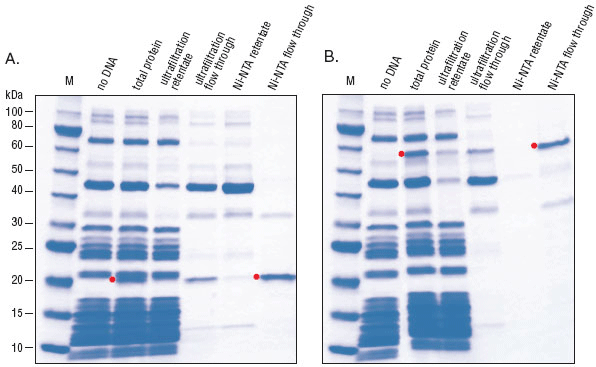
- This product is related to the following categories:
- PURExpress,
- Cell-Free Protein Expression,
- Total RNA Extraction & Purification,
- Protein Expression,
- This product can be used in the following applications:
- PURExpress,
- Cell-Free Protein Expression,
- Protein Expression
Kit Components
Kit Components
The following reagents are supplied with this product:
| NEB # | Component Name | Component # | Stored at (°C) | Amount | Concentration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Properties & Usage
Materials Required but not Supplied
General: 37°C incubatorLabeling: 35S-Methionine (>1000 Ci/mmol recommended, in vitro translation grade)
TCA Precipitation: TCA solutions (25%, 10%), 1 M NaOH, casamino acids, ethanol, glass fiber filters, vacuum filtration manifold
SDS-PAGE: Gels and running buffer, gel apparatus, power supply, gel dryer
Western Blotting: Transfer apparatus, membrane, antibodies and detection reagent
Purification: Ni-NTA Agarose, Amicon Ultra- 0.5 ml, Ultracel- 100K Membrane Centrifugal Filters
Application Features
- Quickly generate analytical amounts of protein for further characterization
- Confirmation of open reading frames
- Examination of the effects of mutations on ORFs
- Generation of truncated proteins to identify active domains and functional residues
- Introduction of modified, unnatural or labeled amino acids
- Epitope mapping
- Expression of toxic proteins
- Ribosome display
- Translation and/or protein folding studies
- In vitro compartmentalization
Related Products
Companion Products
Product Notes
- The DHFR control template is now supplied at 125 ng/µl. Use 2 µl for the positive control reaction. We use 60 pmoles of ribosomes in a standard 25 μl reaction. The supplied control ribosomes are enough for two reactions. Note: Using a smaller amount of ribosomes is possible but the protein yield may be lower. For detailed usage information please refer to the product manual.
- PURExpress Control Template sequence files: Fasta, GenBank
- Storage: All kit components should be stored at -80°C.
References
- Gupta, P., K. Kannan, et al. (2013). Regulation of Gene Expression by Macrolide-Induced Ribosomal Frameshifting. Mol Cell. 52(5), 629-42. PubMedID: 24239289
- Tsai, A., J. Chen, et al. (2013). Observing Prokaryotic Translation Elongation in Real-Time using Single-Molecule Fluorescence. Biophysical Journal. 104(2, Supplement 1), 257a.
- Vazquez-Laslop, N., H. Ramu, et al. (2010). The key function of a conserved and modified rRNA residue in the ribosomal response to the nascent peptide. EMBO J. 29(18), 3108-3117. PubMedID: 20676057
- Vázquez-Laslop, N., H. Ramu, et al. (2011). Nascent peptide-mediated ribosome stalling promoted by antibiotics. Ribosomes. 377-392.
- Gupta, P., S. Sothiselvam, et al. (2013). Deregulation of translation due to post-transcriptional modification of rRNA explains why erm genes are inducible. Nat Commun . 4, 1984. PubMedID: 23749080
- Harvey, C. J., J. D. Puglisi, et al. (2012). Precursor directed biosynthesis of an orthogonally functional erythromycin analogue: selectivity in the ribosome macrolide binding pocket. J Am Chem Soc. 134(29), 12259-65. PubMedID: 22741553
- Kaiser, C. M., D. H. Goldman, et al. (2011). The ribosome modulates nascent protein folding. Science. 334(6063), 1723-7. PubMedID: 22194581
- Kannan, K., N. Vázquez-Laslop, et al. (2012). Selective Protein Synthesis by Ribosomes with a Drug-Obstructed Exit Tunnel. Cell. 151(3), 508-520. PubMedID: 23101624
- Kopaskie, K. S., K. G. Ligtenberg, et al. (2013). Translational regulation of Yersinia enterocolitica mRNA encoding a type III secretion substrate. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 288(49), 35478-88. PubMedID: 24158443
- Martínez, A. K., E. Gordon, et al. (2013). Interactions of the TnaC nascent peptide with rRNA in the exit tunnel enable the ribosome to respond to free tryptophan. Nucleic Acids Research. 42(2), 1245-56. PubMedID: 24137004
- Orelle, C., S. Carlson, et al. (2013). Tools for Characterizing Bacterial Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 57(12), 5994-6004. PubMedID: 24041905
- Shi, W., X. Zhang, et al. (2011). Pyrazinamide inhibits trans-translation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 333(6049), 1630-1632. PubMedID: 21835980
Protocols, Manuals & Usage
Protocols
- Protein Synthesis Reaction using PURExpress (E3313)
- Analysis of Synthesized Protein using PURExpress (E3313)
- Determination of Protein Synthesis Yield with PURExpress (E3313, E6800, E6840, E6850)
- Purification of Synthesized Protein using Reverse His-tag Purification
- Measurement of 35S-Methionine Incorporation by TCA Precipitation and Yield Determination using PURExpress
Manuals
The Product Manual includes details for how to use the product, as well as details of its formulation and quality controls.
Application Notes
Tools & Resources
Selection Charts
FAQs & Troubleshooting
FAQs
- Where can I find many more detailed FAQs for PURExpress?
- How is the Δ Ribosome Kit E3313S different from the PURExpress E6800S kit?
- When using PURExpress, I was able to synthesize the target protein, but full-length product is not major species?
- When using PURExpress, I was unable to synthesize the control protein?
- When using PURExpress, I was able to synthesize the control protein, but the target sample is not present or present in low yield?
- Where can find all IMPACT FAQs?
- Are there PURExpress citations?
Tech Tips
Thoroughly mix solutions A and B before using. Do not vortex Solution B or ribosomes, mix gently.
Solution A may have a cloudy white appearance. Add to the reaction as a uniform suspension.
Assemble the reactions in the following order on ice: Solution A, Solution B, RNAse Inhibitor, Water, Template DNA or RNA
Once reaction is assembled take time to make sure everything is thoroughly mixed by gently pipetting up and down, pulse spin and place at 37C for 2 to 4 hours.
Citations & Technical Literature
Citations
Additional Citations
Quality, Safety & Legal
Quality Assurance Statement
Quality Control tests are performed on each new lot of NEB product to meet the specifications designated for it. Specifications and individual lot data from the tests that are performed for this particular product can be found and downloaded on the Product Specification Sheet, Certificate of Analysis, data card or product manual. Further information regarding NEB product quality can be found here.Specifications
The Specification sheet is a document that includes the storage temperature, shelf life and the specifications designated for the product. The following file naming structure is used to name these document files: [Product Number]_[Size]_[Version]Certificate Of Analysis
The Certificate of Analysis (COA) is a signed document that includes the storage temperature, expiration date and quality controls for an individual lot. The following file naming structure is used to name these document files: [Product Number]_[Size]_[Version]_[Lot Number]- E3313S_v1_10015191
- E3313S_v1_10029437
- E3313S_v1_10042275
- E3313S_v1_10050082
- E3313S_v1_10054527
- E3313S_v1_10065058
- E3313S_v1_10070727
- E3313S_v1_10079359
- E3313S_v1_10090695
- E3313S_v2_10102802
- E3313S_v2_10116018
- E3313S_v2_10124386
- E3313S_v2_10133310
- E3313S_v2_10174658
- E3313S_v2_10181434
- E3313S_v2_10184476
- E3313S_v2_10191799
- E3313S_v2_10195947
- E3313S_v2_10204004
- E3313S_v2_10204924
- E3313S_v1_0161802
- E3313S_v2_10229000
- E3313S_v2_10229779
- E3313S_v2_10243895
- E3313S_v2_10244079
- E3313S_v2_10249335
- E3313S_v2_10256956
- E3313S_v2_10263438
- E3313S_v2_10270617
- E3313S_v2_10276012
- E3313S_v2_10282482
- E3313S_v2_10283828
- E3313S_v2_10293053
- E3313S_v2_10307608
Safety DataSheets
The following is a list of Safety Data Sheet (SDS) that apply to this product to help you use it safely.PURExpress Solution A
Factor Mix (30 μl)
E. coli Ribosome
Control (DHFR) template (10 μl)
Legal and Disclaimers
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.
New England Biolabs (NEB) is committed to practicing ethical science – we believe it is our job as researchers to ask the important questions that when answered will help preserve our quality of life and the world that we live in. However, this research should always be done in safe and ethical manner. Learn more.
Other Products You May Be Interested In
The supporting documents available for this product can be downloaded below.

